How to Optimize React Native Performance for Faster Apps
Fernando Chaves
August 13, 2025

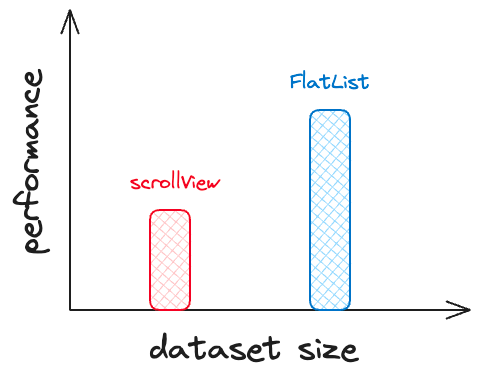
<FlatList
data={items}
keyExtractor={item => item.id}
getItemLayout={(_, index) => ({
length: ITEM_HEIGHT,
offset: ITEM_HEIGHT * index,
index,
})}
renderItem={({item}) => <ItemComponent {...item} />}
/>
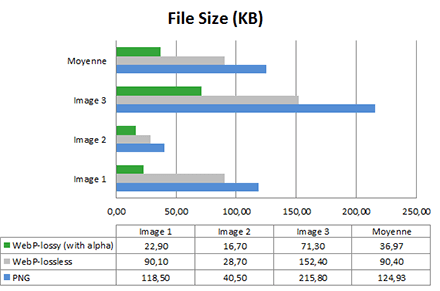
2. Optimize Images and Other Static Assets
<FastImage
style={{width: 200, height: 200}}
source={{
uri: imageUri,
priority: FastImage.priority.normal,
cache: FastImage.cacheControl.cacheOnly,
}}
/>
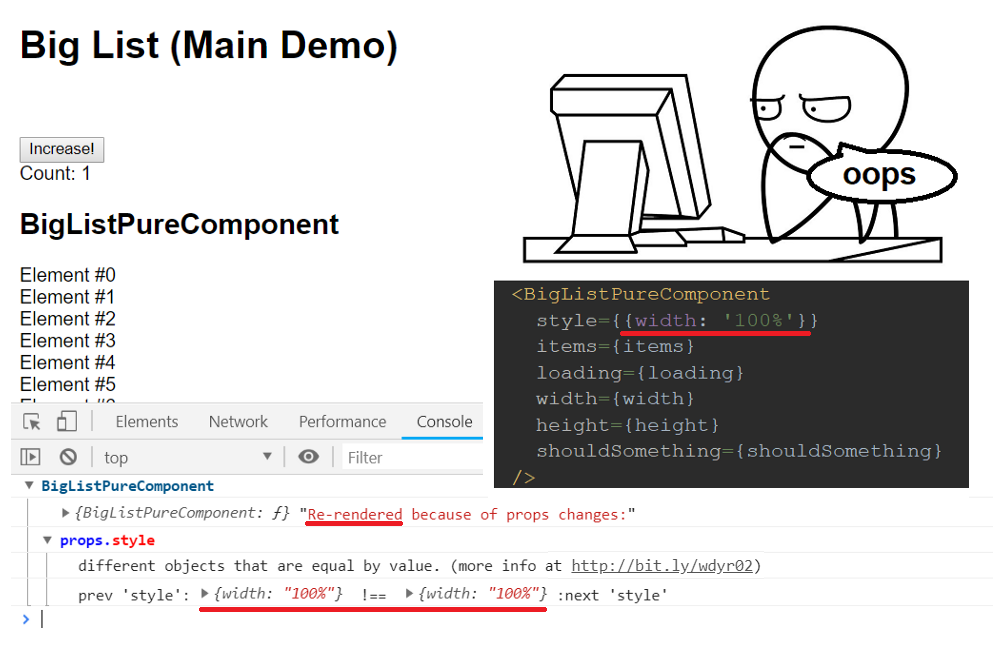
3. Enable Hermes and Adopt the New Architecture
project.ext.react = [
enableHermes: true
]
const MyButton = React.memo(({onPress, label}) => (
<Button onPress={onPress} title={label} />
));
const Parent = () => {
const handlePress = useCallback(() => { /* action */ }, []);
return <MyButton onPress={handlePress} label="Click me" />;
};
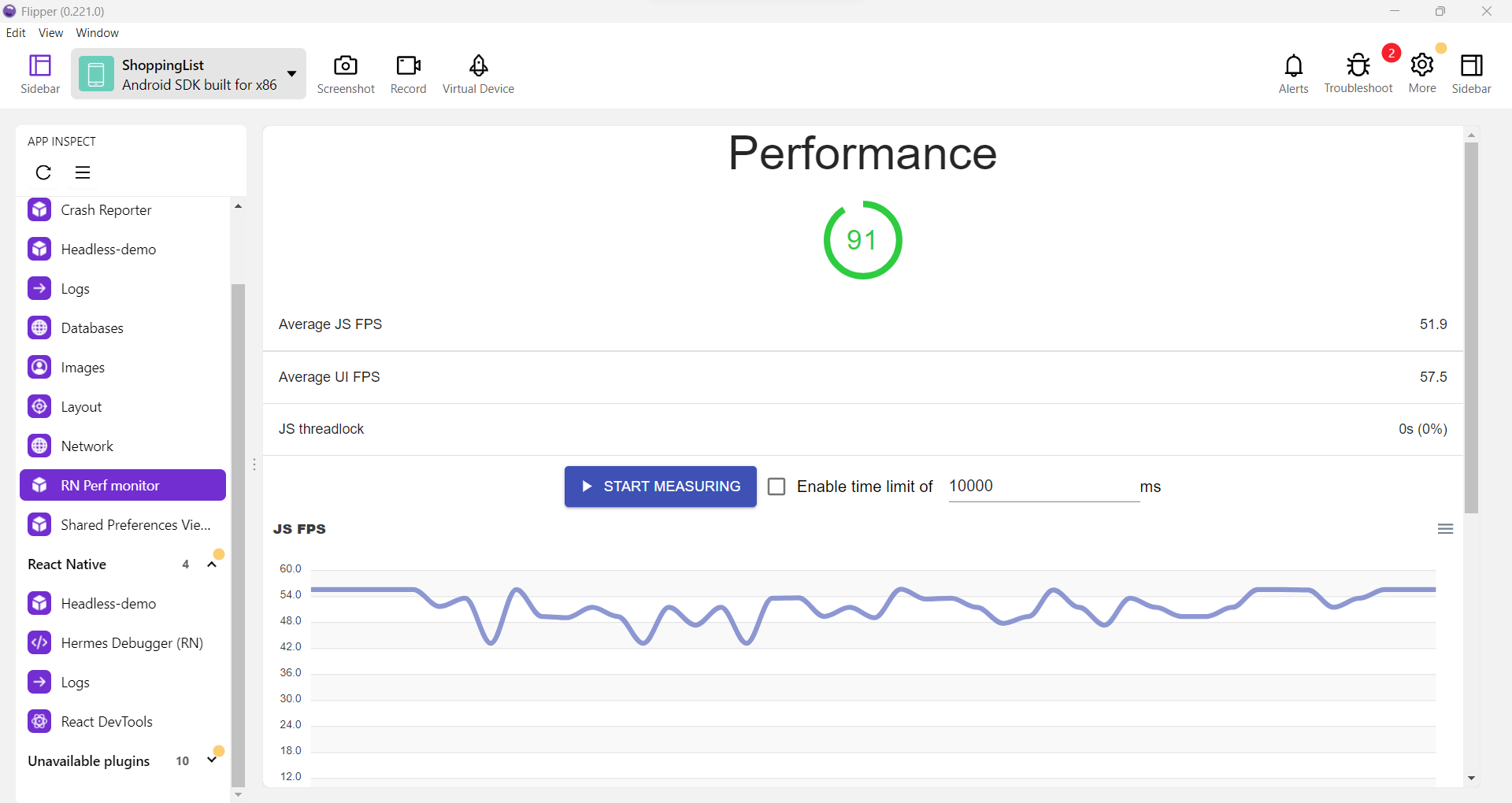
5. Profile and Monitor Performance Regularly
npm install --save-dev babel-plugin-transform-remove-console