React Native Deep Linking: Setup, Testing & Common Mistakes to Avoid

Fernando Chaves
August 22, 2025

Deep links turn a URL into a jump straight to the right screen. A clean react native deeplink setup shortens onboarding, boosts conversion, and connects campaigns to in-app pages without friction. Below is a practical, production-ready guide that covers schemes, iOS Universal Links, Android App Links, navigation wiring, fast testing, and the mistakes that cause most failures.

What deep linking is, in practice
A deep link is a URL that targets a specific route in your app. It can carry params like IDs, filters, or tabs. If the app is installed, it opens the target screen. If not, verified web links can fall back to your site, so users still land somewhere useful.
Fast path first: custom URL scheme
Custom schemes are quick to implement and useful even when you add verified links later.
Expo
Add a scheme to app.json and rebuild the dev client:
{ "expo": { "scheme": "myapp" } }
Now myapp:// links can open your app. Reference: Expo’s Linking guide is concise and accurate for this setup.
Bare React Native
Android AndroidManifest.xml
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:launchMode="singleTask">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<data android:scheme="myapp" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>singleTask lets your existing activity receive new link intents.
iOS Info.plist
<key>CFBundleURLTypes</key>
<array>
<dict>
<key>CFBundleURLSchemes</key>
<array>
<string>myapp</string>
</array>
</dict>
</array>
iOS AppDelegate bridge
import React
override func application(_ app: UIApplication,
open url: URL,
options: [UIApplication.OpenURLOptionsKey : Any] = [:]) -> Bool {
return RCTLinkingManager.application(app, open: url, options: options)
}
override func application(_ application: UIApplication,
continue userActivity: NSUserActivity,
restorationHandler: @escaping ([UIUserActivityRestoring]?) -> Void) -> Bool {
return RCTLinkingManager.application(application, continue: userActivity, restorationHandler: restorationHandler)
}Verified web links for production traffic
iOS Universal Links
Users tap https:// and iOS routes straight into your app if installed.
Steps:
- Add the Associated Domains entitlement, for example
applinks:app.example.com. - Host
https://app.example.com/.well-known/apple-app-site-associationwith allowed paths and your app ID. - Reinstall the app to trigger iOS to fetch and cache the file.
Minimal apple-app-site-association:
{
"applinks": {
"apps": [],
"details": [
{
"appID": "QQ57RJ5UTD.com.example.myapp",
"paths": [ "/product/*", "/profile/*" ]
}
]
}
}Android App Links
Android verifies domain ownership and bypasses the chooser once verified.
Steps:
- Add an intent filter with
http,https, andandroid:autoVerify="true". - Host
https://app.example.com/.well-known/assetlinks.jsonwith your package name and SHA256 cert fingerprint. - Reinstall and allow the device to verify.
Manifest example:
<intent-filter android:autoVerify="true">
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<data android:scheme="https" android:host="app.example.com" />
</intent-filter>assetlinks.json minimal:
[
{
"relation": ["delegate_permission/common.handle_all_urls"],
"target": {
"namespace": "android_app",
"package_name": "com.example.app",
"sha256_cert_fingerprints": ["14:6D:E9:83:...:FF"]
}
}
]
Wire the app: React Navigation and URL mapping
Whether you use Expo or bare, map URLs to screens so both the initial open and subsequent events work.
import * as Linking from 'expo-linking'
import { NavigationContainer } from '@react-navigation/native'
const prefix = Linking.createURL('/') // exp in dev, your scheme in native
const linking = {
prefixes: [prefix, 'https://app.example.com', 'myapp://'],
config: {
screens: {
Home: 'home',
Product: 'product/:id',
Profile: 'profile/:id?',
Settings: 'settings'
}
}
}
export default function App() {
return <NavigationContainer linking={linking}>{/* ... */}</NavigationContainer>
}Prefer one source of truth for paths. Keep your server routes and navigation map in sync.
If you need a manual hook:
import { useEffect } from 'react'
import { Linking } from 'react-native'
export function useDeepLinking(onUrl: (url: string) => void) {
useEffect(() => {
const sub = Linking.addEventListener('url', e => onUrl(e.url))
Linking.getInitialURL().then(u => u && onUrl(u))
return () => sub.remove()
}, [onUrl])
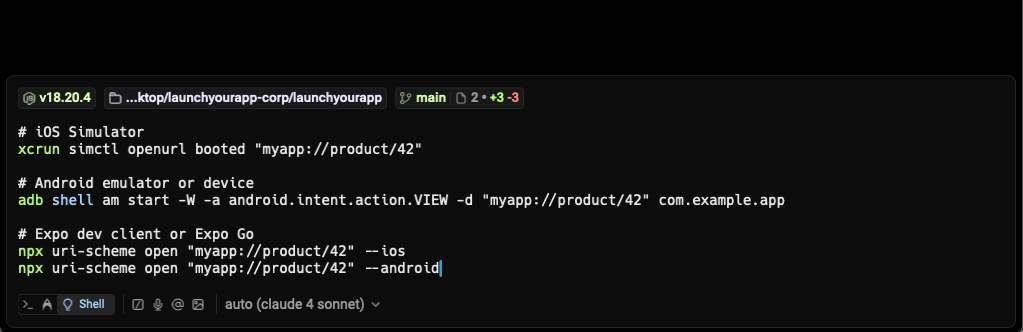
}Testing deep links quickly
Use real taps and commands, not just typing in the address bar.
# iOS Simulator
xcrun simctl openurl booted "myapp://product/42"
# Android emulator or device
adb shell am start -W -a android.intent.action.VIEW -d "myapp://product/42" com.example.app
# Expo dev client or Expo Go
npx uri-scheme open "myapp://product/42" --ios
npx uri-scheme open "myapp://product/42" --androidAdd these to a small script so QA can reproduce with one command.
Analytics, SEO and fallback
- Use
httpslinks for emails, ads, social, and SEO. When the app is not installed, route to the equivalent web page. - Capture
utm_*and custom params so attribution survives the jump from web to app. - If a user is not authenticated, send them through a login that returns to the original deep linked screen.
Common mistakes that break deep links
| Mistake | Symptom | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Missing association files | Links open the browser instead of the app | Publish a valid AASA or assetlinks.json, reinstall, re-verify |
| Scheme only for public traffic | Chooser on Android, poor UX from email | Use verified https links for campaigns |
| No singleTask or iOS bridge | App running but new links are ignored | Add singleTask, wire RCTLinkingManager in AppDelegate |
| Wrong prefixes or path config | Link opens the app but lands on Home | Ensure prefixes and config.screens match every path |
| Stale verification cache | Changes appear to do nothing | Reinstall the app, clear cached association, verify again |
| Ignored query params | Missing filters or state on open | Centralize param parsing and sanitization |
| No error fallback | Broken entity IDs cause blank screens | Route to a safe default with context and retry options |
Troubleshooting checklist
- Confirm the scheme works first, then layer in verified
https. - Log both
Linking.getInitialURL()and theurlevent to see real input. - Curl your AASA or
assetlinks.jsonto verify HTTPS, content type, and JSON. - Validate Associated Domains entitlement and
android:autoVerify. - Map every public path in
config.screens, including nested routes. - Test cold start and warm start, logged in and logged out, slow network and airplane mode.
- Document the canonical link formats for marketing, QA, and support.
Wrap up

Deep linking connects your web, email, and mobile experience without extra taps. Ship a simple scheme for internal use, add Universal Links and App Links for public traffic, map every route, and test with real taps plus command line. Keep verification in your release checklist so links do not silently break.
Want this ready on day one, along with auth, payments, i18n, and polished UI? Use the React Native boilerplate at launchyourapp.dev. It already includes navigation, a sensible linking setup, and patterns for params and fallbacks. Wire your domain, add your screens, and focus on the features that move the needle.

